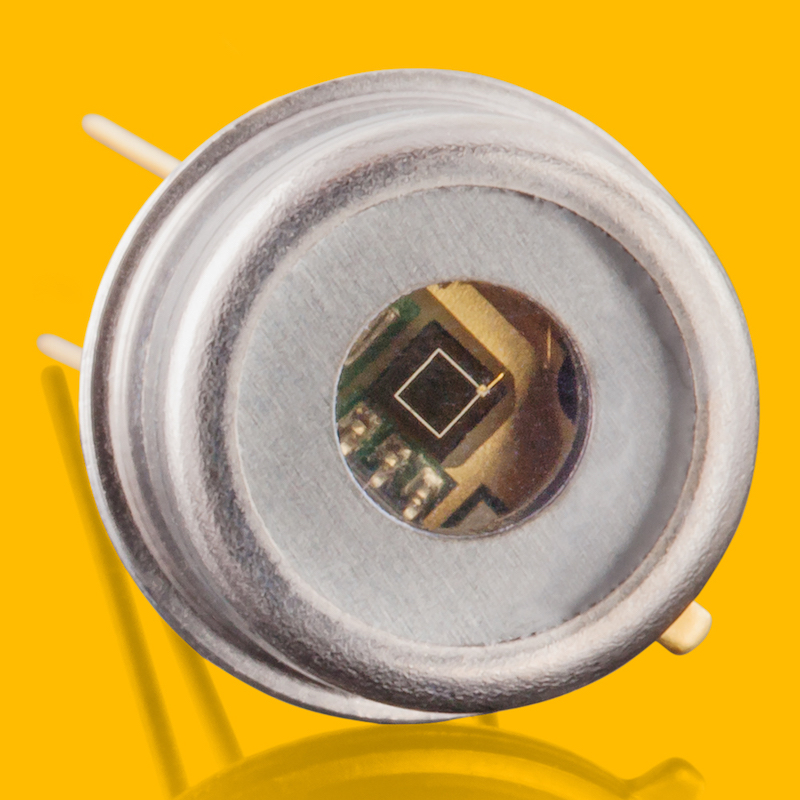
TOCON_C1
- photodétecteur UVC avec amplificateur intégré
- grande puce de détectionSiC de 1 mm² pour maximiser la sensibilité
- structure TO5 encapsulée hermétiquement
- signal de sortie 0 … 5 V
- radiation maximale (limite de saturation) à 254 nm d’environ 180 nW/cm²
- radiation minimale d’environ 18 pW/cm²
Prix unitaire: 162,80€
Pour des quantités plus importantes, n'hésitez pas à nous contacter pour une offre.
Publications
Yuyu Kimura, IR System Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan
This article was first published in the Japanese Journal of Industrial Heating 2025, vol. 62, no. 3, Edition May
Abstrait
Using semiconductor based sensors for flame detection, such as presented with this article can be regarded as a fascinating approach not just with regards on costs and safety. Additionally, looking at environmental and sustainability aspects using semiconductor sensors instead of discharge tubes is a useful tool towards durability and longevity. The possibility of working with two different sensor chips for two different kind of irradiadion (UV and IR) in one small size sensor housing opens up a multitude of new and interesting application possibilities.
¹Fraunhofer IISB, Erlangen, Germany
²sglux GmbH, Berlin, Germany
Towards SiC-Based VUV Pin-Photodiodes – Investigations on 4H-SiC Photodiodes with Shallow Implanted Al Emitters
Zusammenfassung
4H silicon carbide (SiC) based pin photodiodes with a sensitivity in the vacuum ultraviolet spectrum (VUV) demand newly developed emitter doping profiles. This work features the first ever reported 4H-SiC pin photodiodes with an implanted p-emitter and a noticeable sensitivity at a wavelength of 200 nm. As a first step, Aluminum doping profiles produced by low energy ion implantation in 4H-SiC were characterized by secondary-ion mass spectrometry (SIMS). Photodiodes using these shallow emitters are compared to one with a deep p-emitter doping profile employing IV characteristics and the spectral response. SIMS results demonstrate the possibility of shallow Alimplantation profiles using low implantation energies with all emitter profiles featuring characteristic I-V results. For some shallow doping profiles, a meassurable signal at the upper limit of the VUV spectrum could be demonstrated, paving the way towards 4H-SiC pin photodiodes with sensitivities for wavelengths below 200 nm.
How to determine the right UV sensor for flame detection?
Abstract
The present article informs about different approaches using UV photodetectors for the detection of a combustion flame (natural gas, hydrogen or oil).
TOCONs for the detection of fire and combustion burner flames
TOCONs for the detection of fire and combustion burner flames
Abstract
The standard sglux TOCONs are featured by a relatively high time constant that extends from 30 ms (low sensitivity TOCONs) until 80 ms (high sensitivity TOCONs). Most of the TOCON applications benefit from this high time constant because usually the TOCON’s application is to measure a UV irradiation that slowly changes. Such applications are e.g. the control of UV disinfection and UV curing sources. Short changes of signal caused by electromagnetic or high frequency influences are averaged – which is a benefit. However, looking at flame detection in heaters or looking at fire detection applications this relatively high time constant may cause problems. The present report presents opportunities to reduce the dead time of the TOCONs.
Master Thesis
Abstract
As a contribution to the decarbonisation of domestic heating, the graduation project investigates the feasibility of the application of UV sensor technology for flame detection and flame monitoring in hydrogen-powered domestic gas boilers. The research includes empirical studies and an analytical approach to describe influences on the sensor signal strength.
UV sensors for hydrogen flame detection
Abstract
Bei der Arbeit am gesellschaftlichen Ziel der Dekarbonisierung des Energieverbrauchs u.a. auch durch die Substitution von Erdgas durch regenerativ erzeugte Brennstoffe, ist Wasserstoff ein besonders aussichtsreicher Kandidat. Bei der erforderlichen Umrüstung von Erdgas-Thermen stellt die durch die Norm EN298 definierte Überwachung der Brennerflamme eine besondere Herausforderung dar. Stand der Technik ist die Flammenüberwachung mittels Ionisationsfühlern. Dieses Verfahren ist preiswert und zuverlässig. Wird dem Erdgas allerdings Wasserstoff beigemischt oder besteht das Gas ausschließlich aus Wasserstoff, ergibt sich eine andere Reaktionskinetik, welche die Zuverlässigkeit der bisherigen Fühler deutlich reduziert bzw. ihren Einsatz unmöglich macht.

